LeetCode 第 784 题:“字母大小写全排列”题解
题解地址:深度优先遍历、回溯算法(Python 代码、Java 代码)。
说明:文本首发在力扣的题解版块,更新也会在第 1 时间在上面的网站中更新,这篇文章只是上面的文章的一个快照,您可以点击上面的链接看到其他网友对本文的评论。
传送门:784. 字母大小写全排列。
给定一个字符串S,通过将字符串S中的每个字母转变大小写,我们可以获得一个新的字符串。返回所有可能得到的字符串集合。
示例: 输入: S = "a1b2" 输出: ["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
输入: S = "3z4" 输出: ["3z4", "3Z4"]
输入: S = "12345" 输出: ["12345"] 注意:
S 的长度不超过12。 S 仅由数字和字母组成。
##深度优先遍历、回溯算法(Python 代码、Java 代码)
思路分析:
1、思路:搜索、backtrack
按照我的经验来看,这类搜索问题的思路就是画树形图,这个树形图一般也是递归结构,然后看着图把代码写出来。说起来比较简单,但是也是需要一定的代码积累。
另外说一下,回溯的问题,这道题居然被标为“简单”,也是非常神奇的一件事情。
(温馨提示:下面的幻灯片中,有几页上有较多的文字,可能需要您停留一下,可以点击右下角的后退 “|◀” 或者前进 “▶|” 按钮控制幻灯片的播放。)

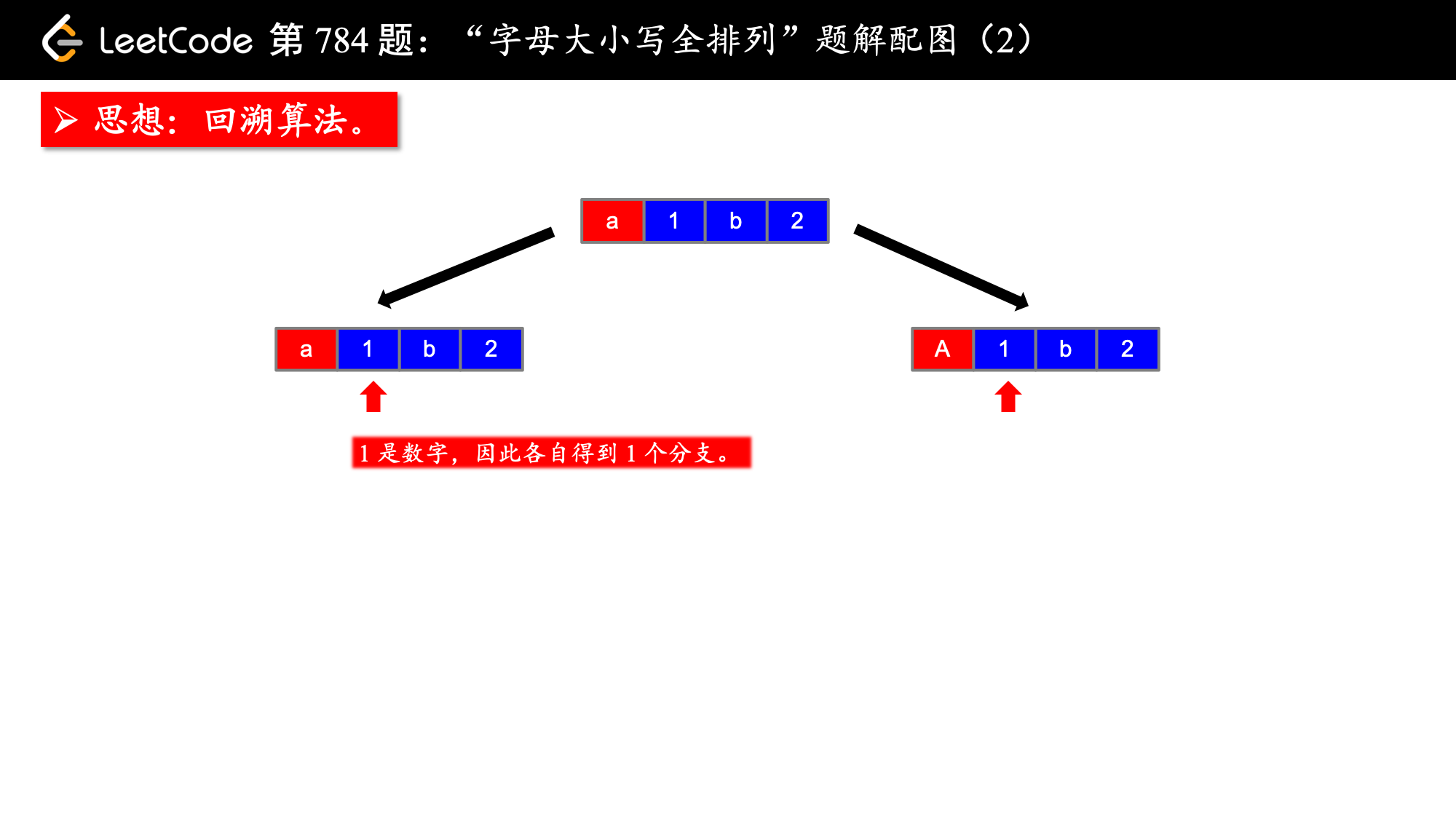
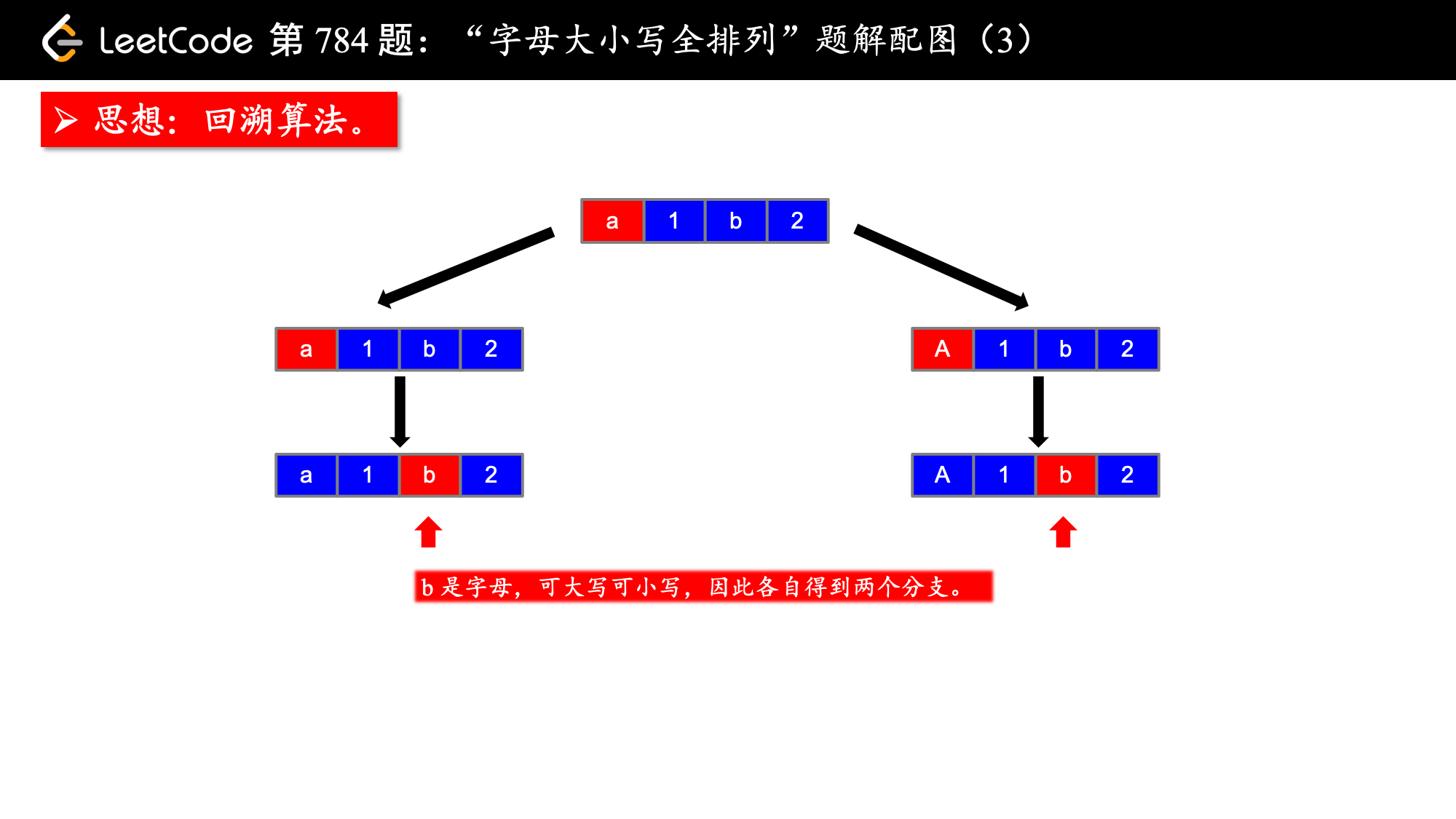
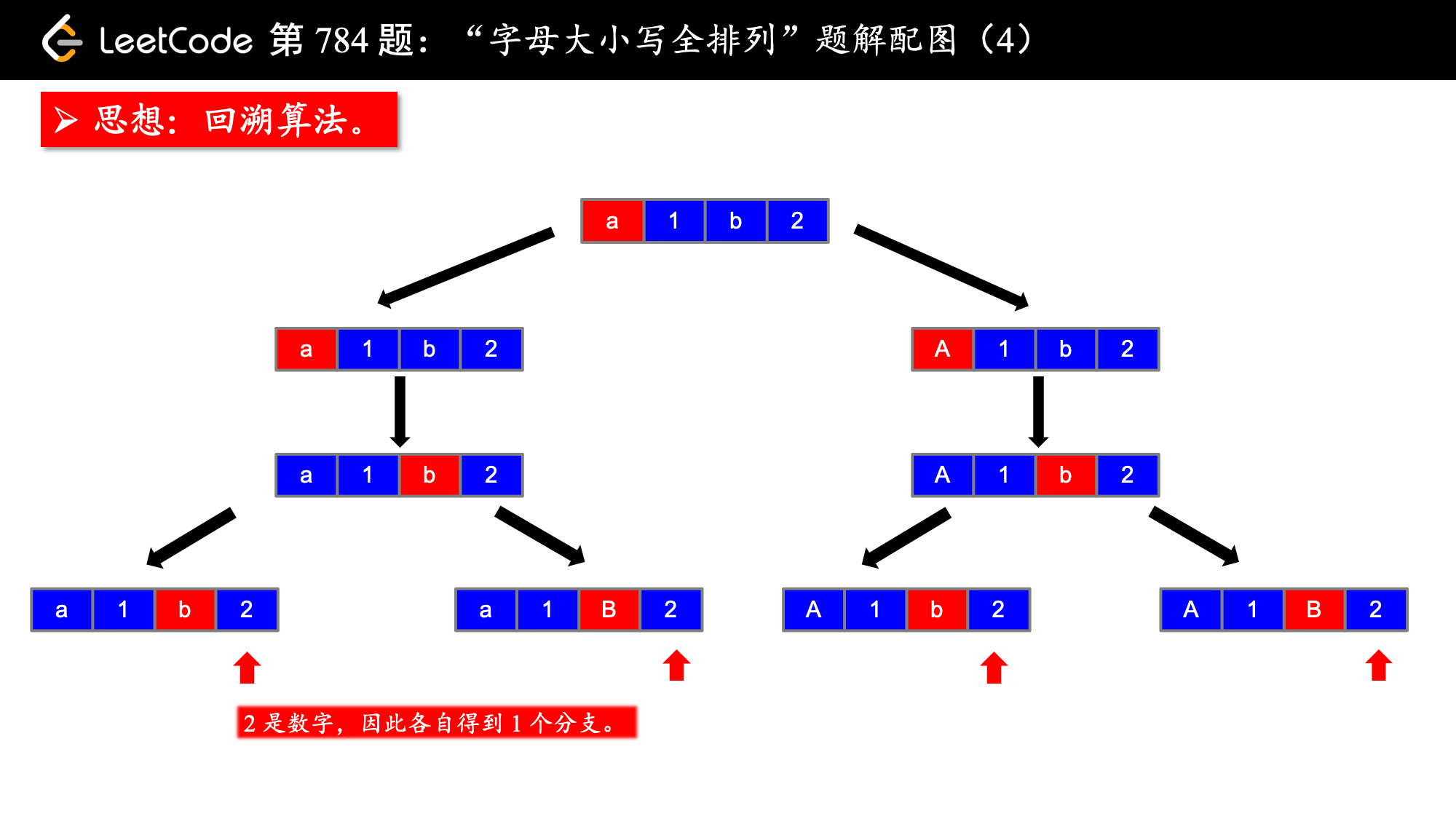
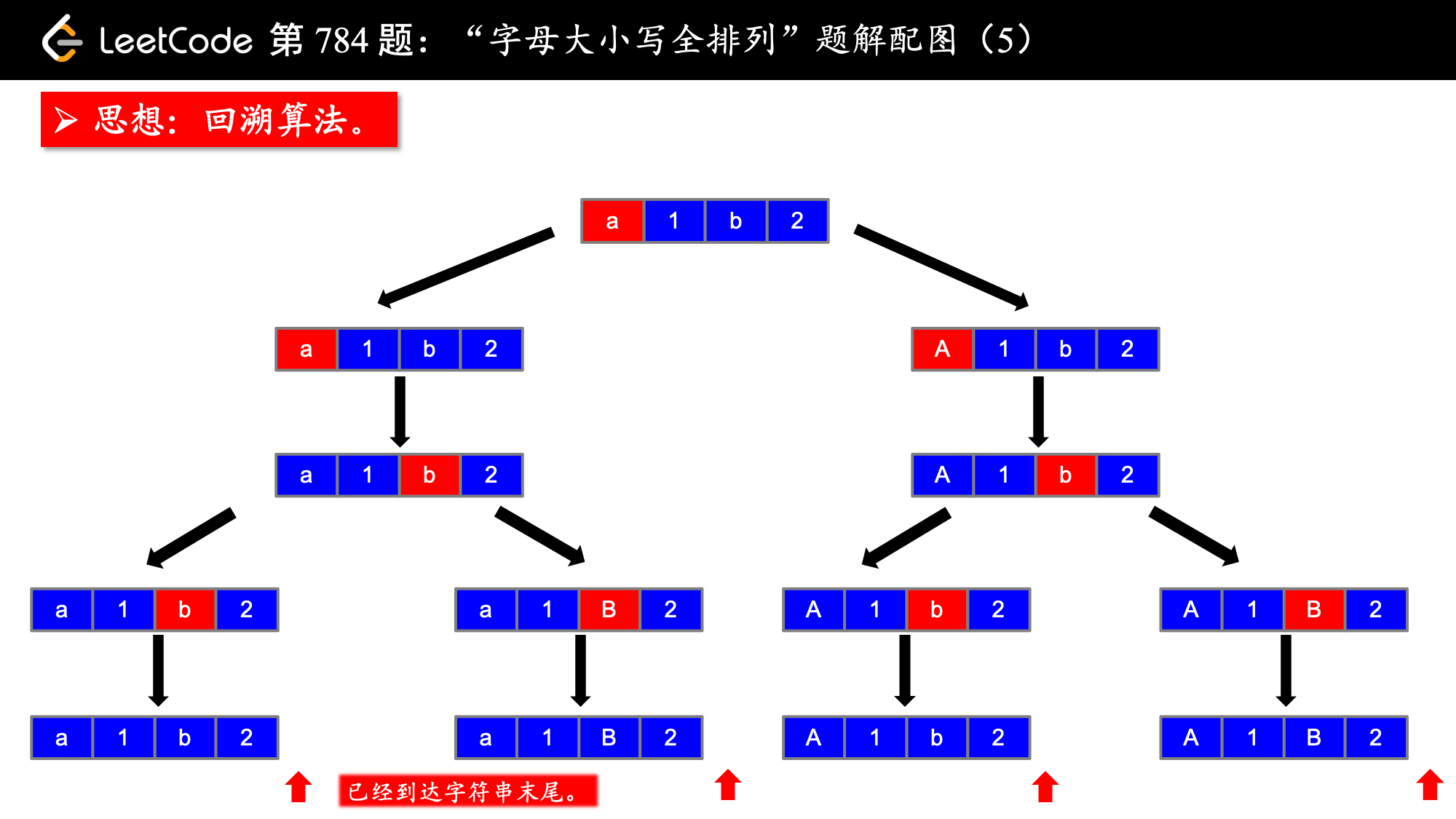
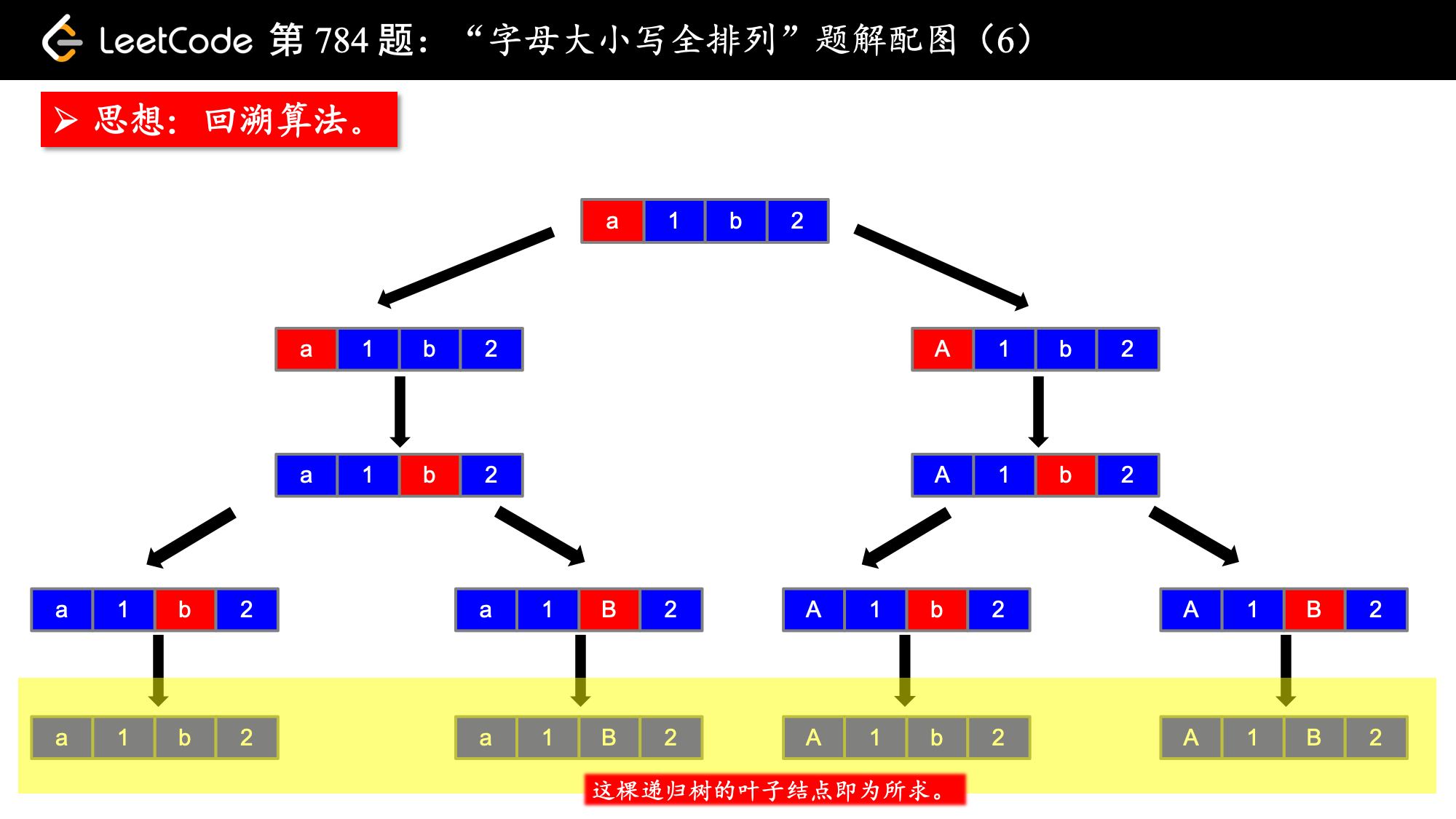
思路搞定了,下面要介绍一个技巧,即解决字母大小写转换的问题。
2、技巧:使用异或运算转换字母大小写
这一步比较有技巧,我也是参考了别人的思路,用自己话写了出来。
我们先看一看 ASCII 表,A 到 Z,Z 完了以后没有直接到 a,中间隔了 6 个字符。
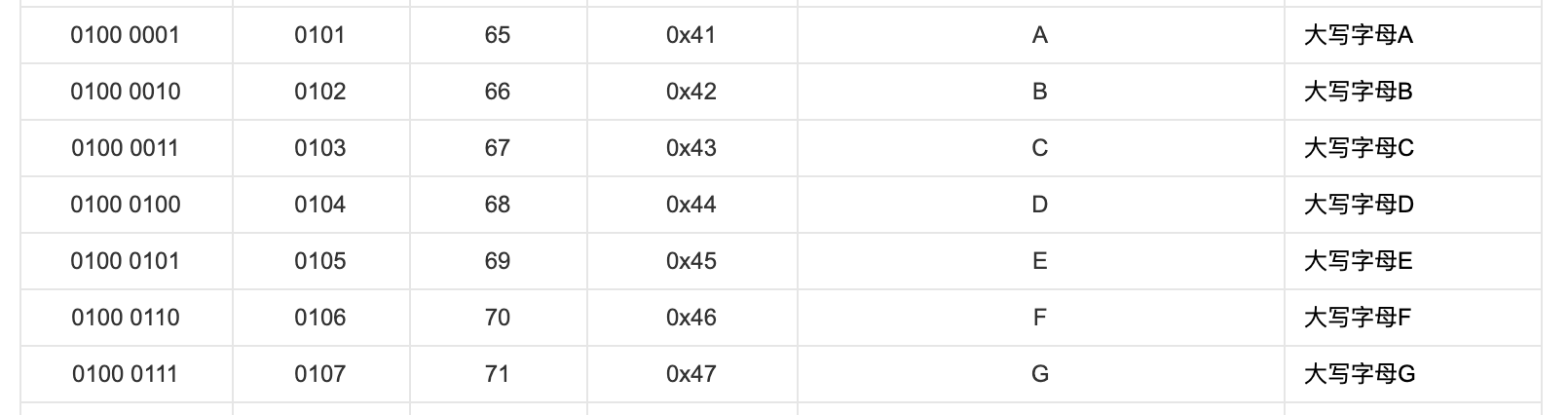
(中间省略)
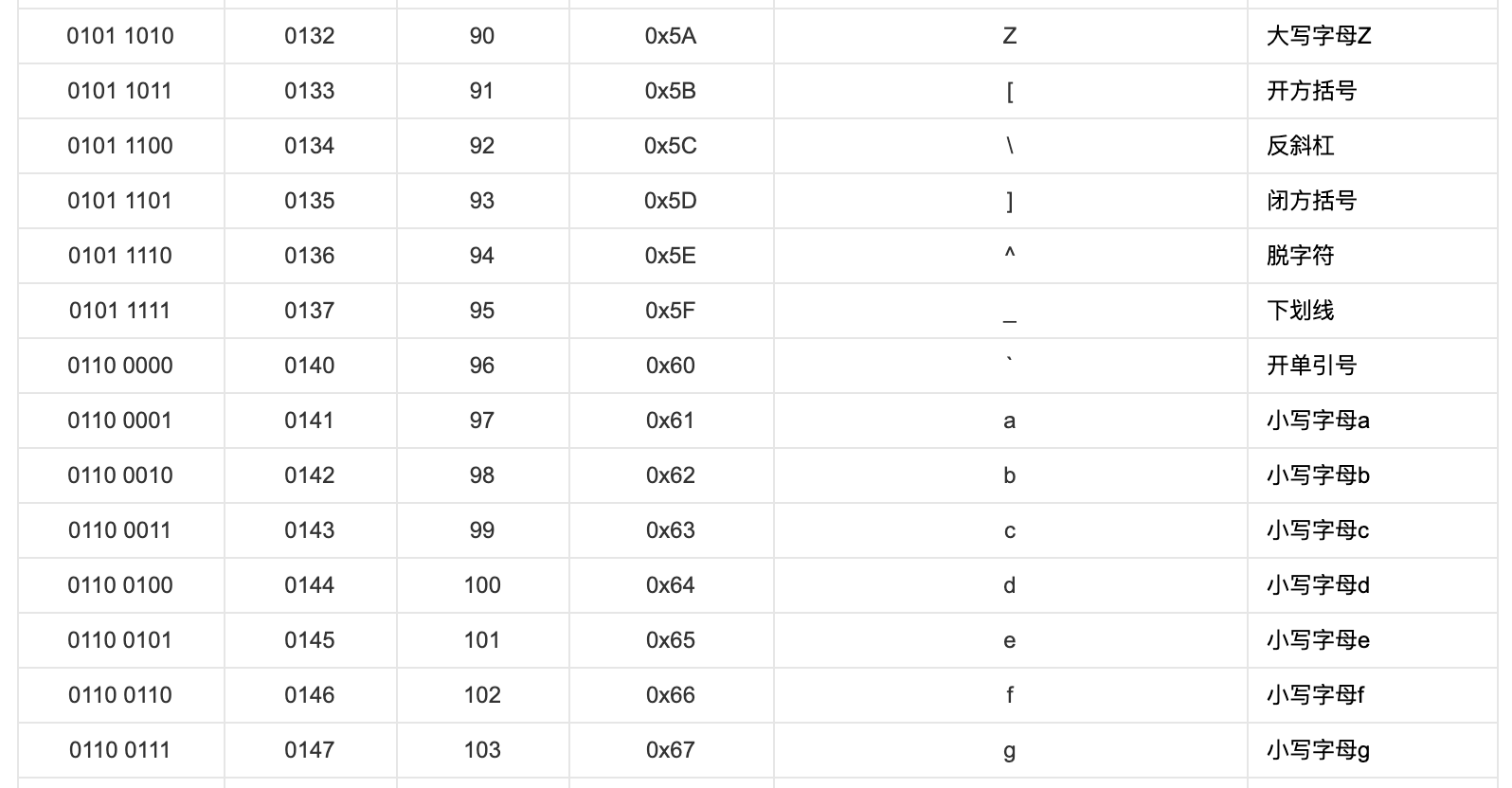
我们发现大写字符与其对应的小写字符的 ASCII 的差为 32,32 这个值如果敏感的话,它是 ,在编程语言中,可以表示为 1 << 5。而
变换大小写这件事等价于:
1、如果字符是小写字符,减去 32 得到大写字符;
2、如果字符是大写字符,加上 32 得到小写字符。
而这两者合并起来,就是给这个字符做一次不进位的加法,即异或上 1 << 5。
参考代码 1:使用回溯问题经常使用的 path 变量,在叶子结点处结算
Python 代码:
from typing import List
class Solution:
def letterCasePermutation(self, S: str) -> List[str]:
size = len(S)
if size == 0:
return []
res = []
path = []
self.__dfs(S, size, 0, path, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, S, size, index, path, res):
if index == size:
return res.append(''.join(path))
path.append(S[index])
self.__dfs(S, size, index + 1, path, res)
path.pop()
# 如果是字母,就变换大小写
if S[index].isalpha():
path.append(chr(ord(S[index]) ^ (1 << 5)))
self.__dfs(S, size, index + 1, path, res)
path.pop()
Java 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @author liwei
* @date 2019/7/16 9:27 PM
*/
public class Solution4 {
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String S) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 特判
int len = S.length();
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
Stack<Character> path = new Stack<>();
dfs(S, 0, len, path, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(String S, int index, int len, Stack<Character> stack, List<String> res) {
if (index == len) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
stringBuilder.append(stack.get(i));
}
res.add(stringBuilder.toString());
return;
}
stack.add(S.charAt(index));
dfs(S, index + 1, len, stack, res);
stack.pop();
if (Character.isLetter(S.charAt(index))) {
stack.add((char) (S.charAt(index) ^ (1 << 5)));
dfs(S, index + 1, len, stack, res);
stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String S = "a1b2";
List<String> letterCasePermutation = solution.letterCasePermutation(S);
System.out.println(letterCasePermutation);
}
}
参考代码 2:传入字符数组,也是在叶子结点处结算。
Python 代码:
from typing import List
class Solution:
def letterCasePermutation(self, S: str) -> List[str]:
size = len(S)
if size == 0:
return []
res = []
arr = list(S)
self.__dfs(arr, size, 0, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, arr, size, index, res):
if index == size:
return res.append(''.join(arr))
# 先把当前加到 pre 里面
self.__dfs(arr, size, index + 1, res)
# 如果是字母,就变换大小写
if arr[index].isalpha():
arr[index] = chr(ord(arr[index]) ^ (1 << 5))
self.__dfs(arr, size, index + 1, res)
Java 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author liwei
* @date 2019/7/16 9:27 PM
*/
public class Solution3 {
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String S) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 特判
int len = S.length();
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
char[] chars = S.toCharArray();
dfs(0, len, chars, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int index, int len, char[] chars, List<String> res) {
if (index == len) {
res.add(new String(chars));
return;
}
dfs(index + 1, len, chars, res);
if (Character.isLetter(chars[index])) {
chars[index] ^= (1 << 5);
dfs(index + 1, len, chars, res);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String S = "a1b2";
List<String> letterCasePermutation = solution.letterCasePermutation(S);
System.out.println(letterCasePermutation);
}
}