LeetCode 第 140 题:“单词拆分 II”题解
题解地址:“动态规划 + 回溯”求解具体值(Python 代码、Java 代码)。
说明:文本首发在力扣的题解版块,更新也会在第 1 时间在上面的网站中更新,这篇文章只是上面的文章的一个快照,您可以点击上面的链接看到其他网友对本文的评论。
传送门:140. 单词拆分 II。
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,在字符串中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。返回所有这些可能的句子。
说明:
分隔时可以重复使用字典中的单词。 你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。 示例 1:
输入: s = "catsanddog" wordDict = ["cat", "cats", "and", "sand", "dog"] 输出: [ "cats and dog", "cat sand dog" ] 示例 2:
输入: s = "pineapplepenapple" wordDict = ["apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"] 输出: [ "pine apple pen apple", "pineapple pen apple", "pine applepen apple" ] 解释: 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。 示例 3:
输入: s = "catsandog" wordDict = ["cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"] 输出: []
“动态规划 + 回溯”求解具体值(Python 代码、Java 代码)
本题是「力扣」第 139 题:单词拆分的后序问题,本题解基于该问题的题解《动态规划(Python 代码、Java 代码)》编写而成,需要先阅读该题解,才能理解本题解的内容。
我们就接着使用上一题的到的动态规划的状态数组来解答这个问题。
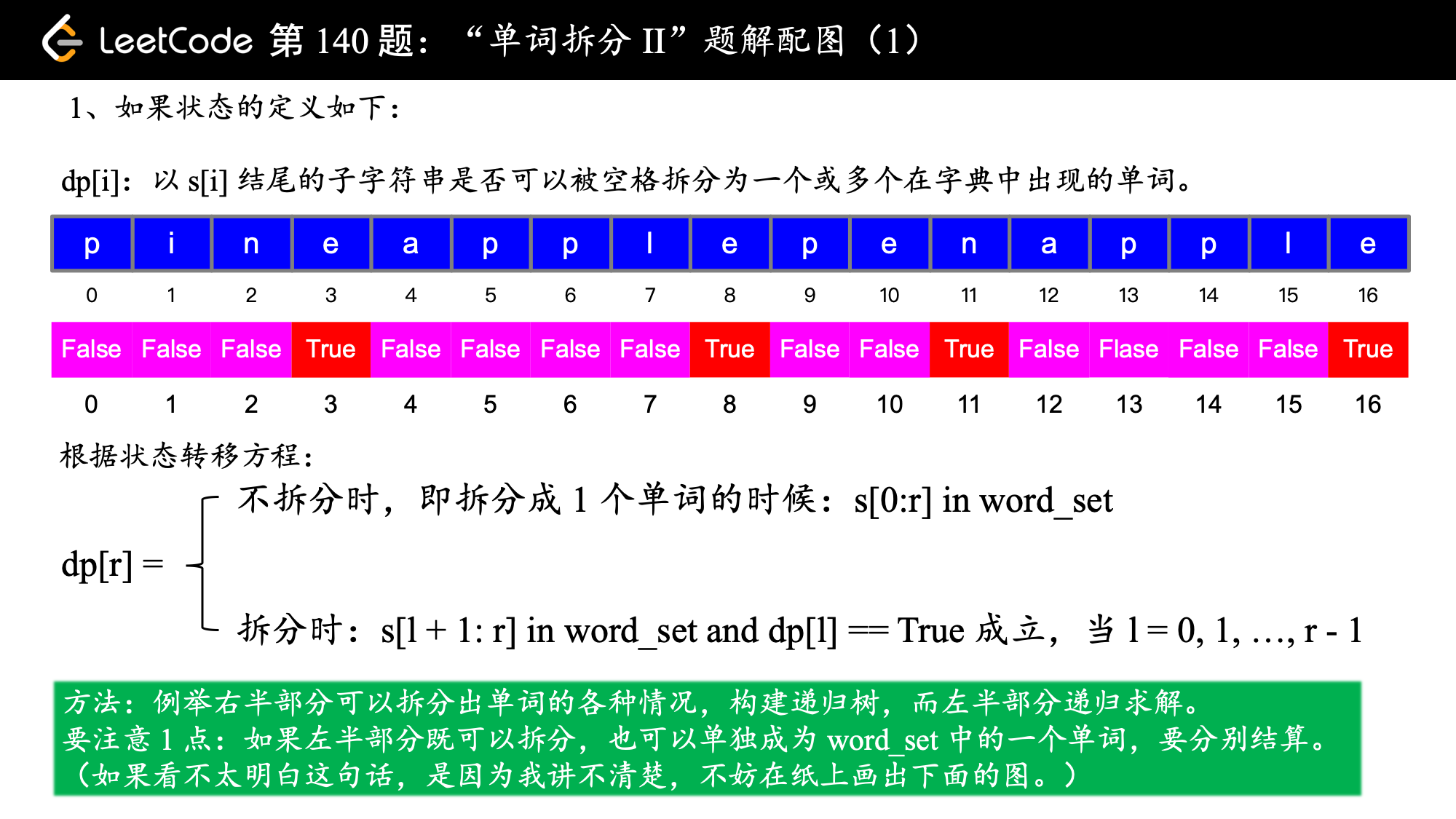
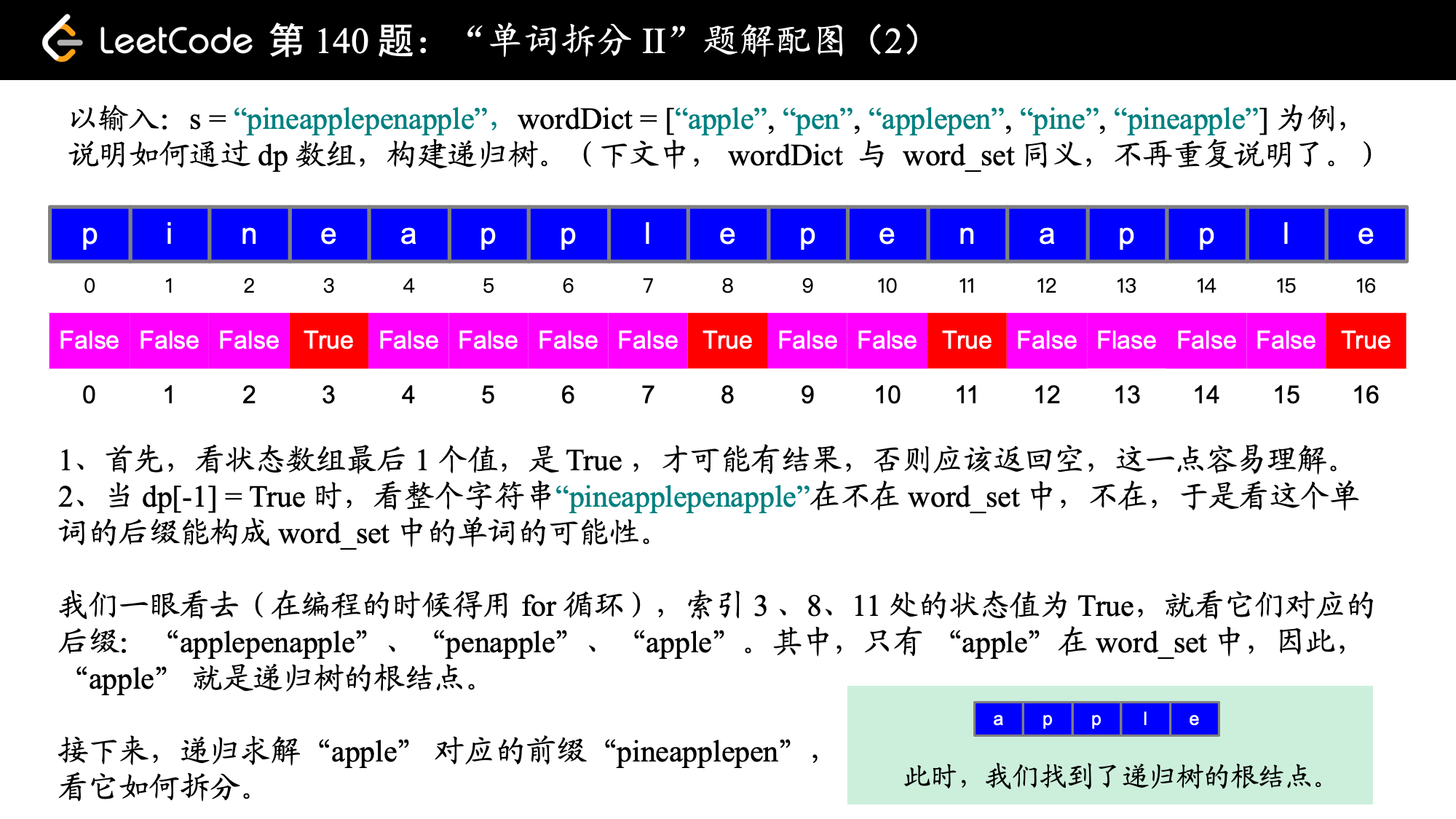
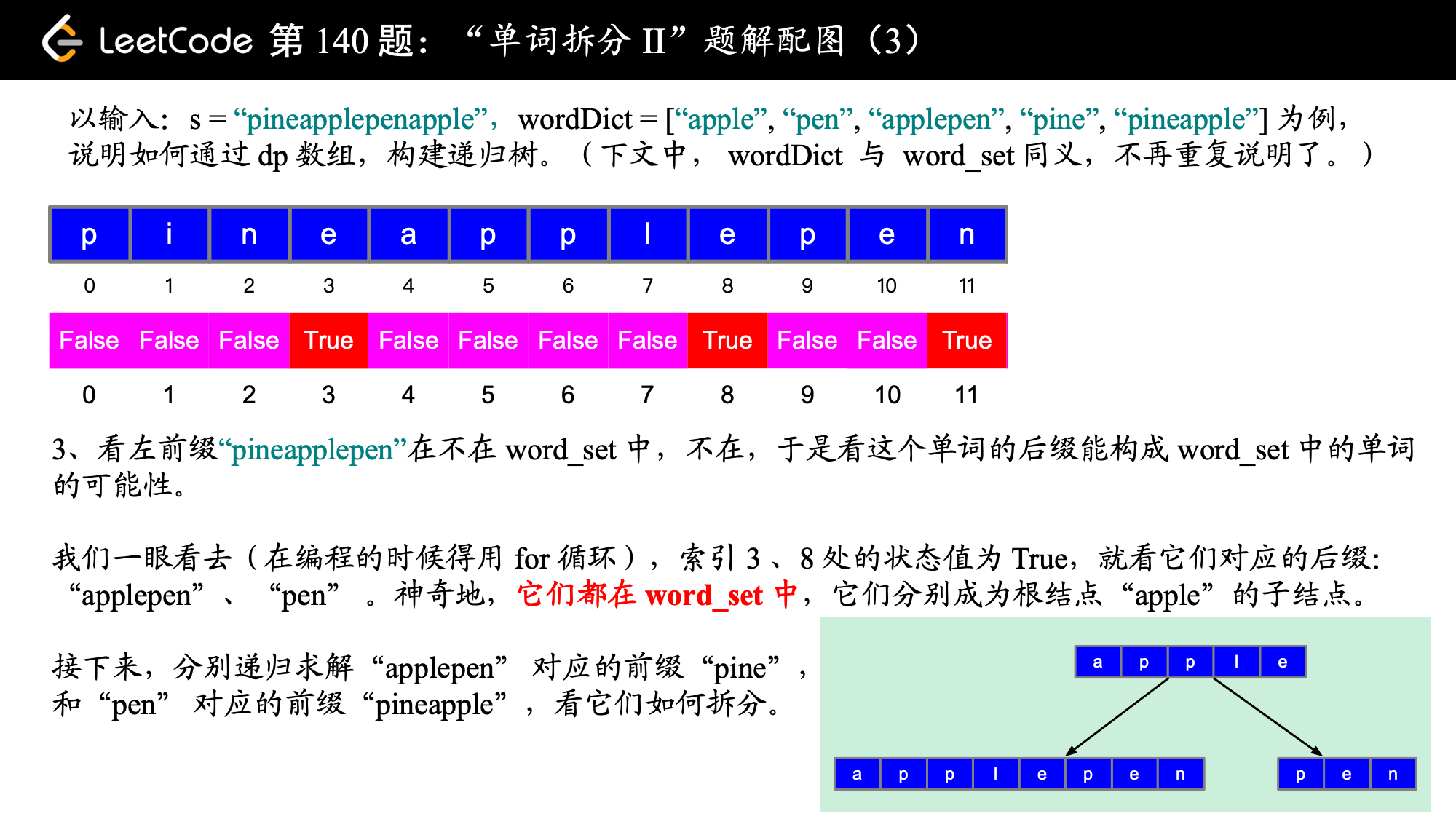
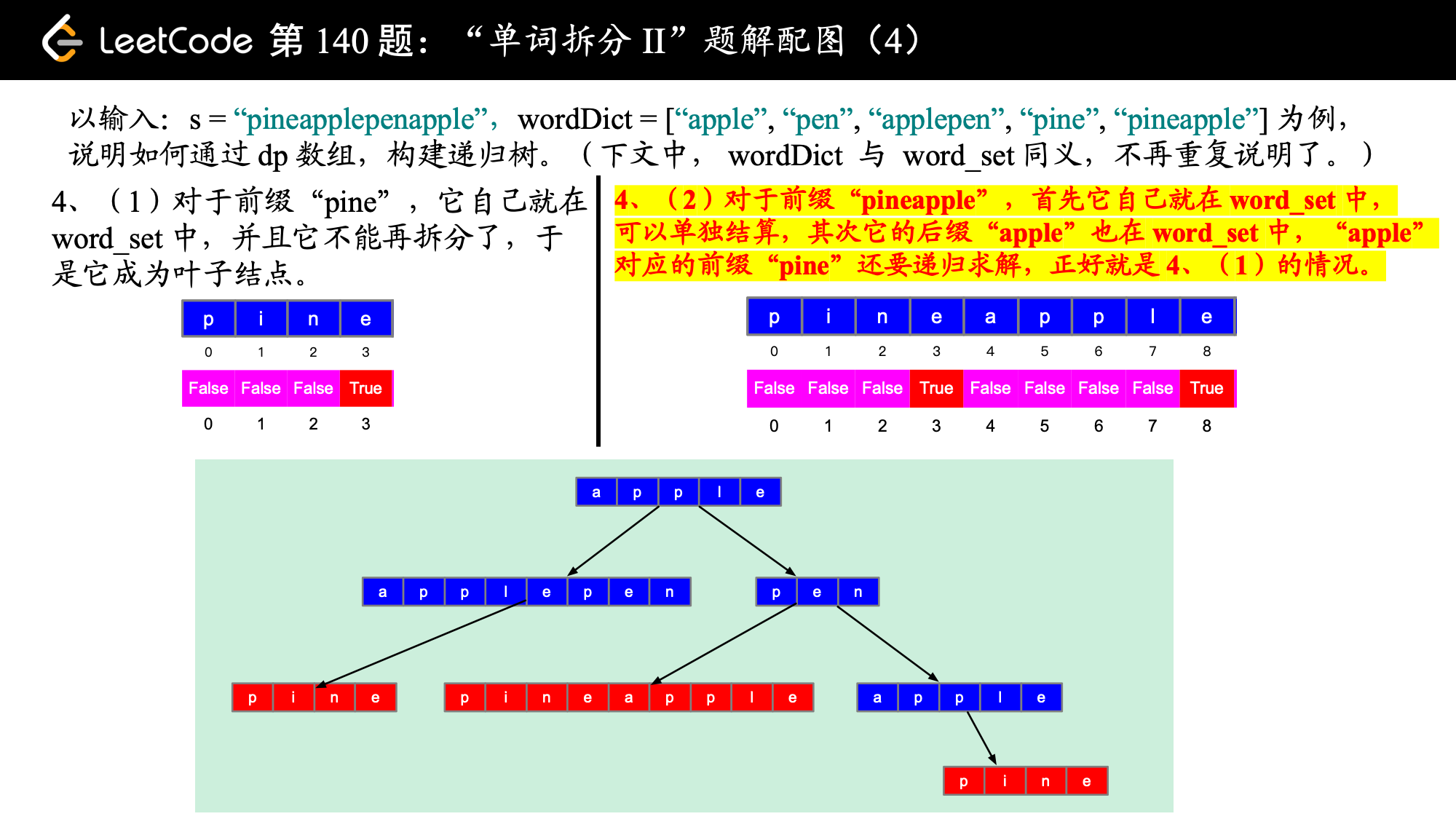
参考代码 1:状态的定义为:以 s[i] 结尾的子字符串是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
Python 代码:
from typing import List
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def wordBreak(self, s: str, wordDict: List[str]) -> List[str]:
size = len(s)
# 题目中说非空字符串,以下 assert 一定通过
assert size > 0
# 预处理,把 wordDict 放进一个哈希表中
word_set = {word for word in wordDict}
# print(word_set)
# 状态:以 s[i] 结尾
# 这种状态定义很常见
dp = [False for _ in range(size)]
dp[0] = s[0] in word_set
# print(dp)
# 使用 r 表示右边界,可以取到
# 使用 l 表示左边界,也可以取到
for r in range(1, size):
# Python 的语法,在切片的时候不包括右边界
# 如果整个单词就直接在 word_set 中,直接返回就好了
# 否则把单词做分割,挨个去判断
if s[:r + 1] in word_set:
dp[r] = True
continue
for l in range(r):
# dp[l] 写在前面会更快一点,否则还要去切片,然后再放入 hash 表判重
if dp[l] and s[l + 1: r + 1] in word_set:
dp[r] = True
# 这个 break 很重要,一旦得到 dp[r] = True ,循环不必再继续
break
res = []
# 如果有解,才有必要回溯
if dp[-1]:
queue = deque()
self.__dfs(s, size - 1, wordDict, res, queue, dp)
return res
def __dfs(self, s, end, word_set, res, path, dp):
# print('刚开始', s[:end + 1])
# 如果不用拆分,整个单词就在 word_set 中就可以结算了
if s[:end + 1] in word_set:
path.appendleft(s[:end + 1])
res.append(' '.join(path))
path.popleft()
for i in range(end):
if dp[i]:
suffix = s[i + 1:end + 1]
if suffix in word_set:
path.appendleft(suffix)
self.__dfs(s, i, word_set, res, path, dp)
path.popleft()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# s = "leetcode"
# wordDict = ["leet", "code"]
s = "pineapplepenapple"
wordDict = ["apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"]
# s = "a"
# wordDict = ["a"]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.wordBreak(s, wordDict)
print(result)
# ["pine apple pen apple","pineapple pen apple","pine applepen apple"]
Java 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class Solution {
public List<String> wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
int len = s.length();
// 状态定义:以 s[i] 结尾的子字符串是否符合题意
boolean[] dp = new boolean[len];
// 预处理
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : wordDict) {
wordSet.add(word);
}
// 动态规划问题一般都有起点,起点也相对好判断一些
// dp[0] = wordSet.contains(s.charAt(0));
for (int r = 0; r < len; r++) {
if (wordSet.contains(s.substring(0, r + 1))) {
dp[r] = true;
continue;
}
for (int l = 0; l < r; l++) {
// dp[l] 写在前面会更快一点,否则还要去切片,然后再放入 hash 表判重
if (dp[l] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(l + 1, r + 1)) ) {
dp[r] = true;
// 这个 break 很重要,一旦得到 dp[r] = True ,循环不必再继续
break;
}
}
}
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (dp[len - 1]) {
LinkedList<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(s, len - 1, wordSet, res, queue, dp);
return res;
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(String s, int end, Set<String> wordSet, List<String> res, LinkedList<String> queue, boolean[] dp) {
if (wordSet.contains(s.substring(0, end + 1))) {
queue.addFirst(s.substring(0, end + 1));
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (String word : queue) {
stringBuilder.append(word);
stringBuilder.append(" ");
}
stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(stringBuilder.length() - 1);
res.add(stringBuilder.toString());
queue.removeFirst();
}
for (int i = 0; i < end; i++) {
if (dp[i]) {
String suffix = s.substring(i + 1, end + 1);
if (wordSet.contains(suffix)) {
queue.addFirst(suffix);
dfs(s, i, wordSet, res, queue, dp);
queue.removeFirst();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "pineapplepenapple";
List<String> wordDict = new ArrayList<>();
wordDict.add("apple");
wordDict.add("pen");
wordDict.add("applepen");
wordDict.add("pine");
wordDict.add("pineapple");
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<String> res = solution.wordBreak(s, wordDict);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
参考代码 2:状态:dp[i] 表示子串 s[0:i] (即长度为 i 的子串,其实就是前缀)可以被空格拆分,并且拆分以后的单词是否落在 wordDict 中。
Python 代码:
from typing import List
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def wordBreak(self, s: str, wordDict: List[str]) -> List[str]:
size = len(s)
# 题目中说非空字符串,以下 assert 一定通过
assert size > 0
# 预处理,把 wordDict 放进一个哈希表中
word_set = {word for word in wordDict}
# dp[i] 表示长度为 i 的 s,满足题意
# 0 表示 False ,1 表示 True
dp = [0 for _ in range(size + 1)]
dp[0] = 1
for i in range(1, size + 1):
# i 表示 s 子串的长度
for j in range(i):
# j 表示后子串的起始位置,最多到 i-1
# j 也正正好表示前子串的长度
# dp[j] 写在前面会更快一点,否则还要去切片,然后再放入 hash 表判重
if dp[j] and s[j:i] in word_set:
dp[i] = 1
break
res = []
# 如果有解,才有必要回溯
if dp[-1]:
queue = deque()
self.__dfs(s, size, word_set, res, queue, dp)
return res
def __dfs(self, s, length, word_set, res, path, dp):
if length == 0:
res.append(' '.join(path))
return
for i in range(length):
if dp[i]:
suffix = s[i:length]
if suffix in word_set:
path.appendleft(suffix)
self.__dfs(s, i, word_set, res, path, dp)
path.popleft()
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "pineapplepenapple"
wordDict = ["apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.wordBreak(s, wordDict)
print(result)
Java 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class Solution2 {
public List<String> wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
int len = s.length();
// 状态定义:长度为 i 的子字符串是否符合题意
boolean[] dp = new boolean[len + 1];
// 预处理
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : wordDict) {
wordSet.add(word);
}
// 这个状态的设置非常关键,说明前部分的字符串已经在 wordSet 中
dp[0] = true;
for (int r = 1; r < len + 1; r++) {
for (int l = 0; l < r; l++) {
// dp[l] 写在前面会更快一点,否则还要去切片,然后再放入 hash 表判重
if (dp[l] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(l, r)) ) {
dp[r] = true;
// 这个 break 很重要,一旦得到 dp[r] = True ,循环不必再继续
break;
}
}
}
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (dp[len]) {
LinkedList<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(s, len, wordSet, res, queue, dp);
return res;
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(String s, int end, Set<String> wordSet, List<String> res, LinkedList<String> queue, boolean[] dp) {
if (end == 0) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (String word : queue) {
stringBuilder.append(word);
stringBuilder.append(" ");
}
stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(stringBuilder.length() - 1);
res.add(stringBuilder.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < end; i++) {
if (dp[i]) {
String suffix = s.substring(i, end);
if (wordSet.contains(suffix)) {
queue.addFirst(suffix);
dfs(s, i, wordSet, res, queue, dp);
queue.removeFirst();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "pineapplepenapple";
List<String> wordDict = new ArrayList<>();
wordDict.add("apple");
wordDict.add("pen");
wordDict.add("applepen");
wordDict.add("pine");
wordDict.add("pineapple");
Solution2 solution2 = new Solution2();
List<String> res = solution2.wordBreak(s, wordDict);
System.out.println(res);
}
}