LeetCode 第 46 题:“全排列”题解
题解地址:回溯算法 + 位掩码(Python 代码、Java 代码)。
说明:文本首发在力扣的题解版块,更新也会在第 1 时间在上面的网站中更新,这篇文章只是上面的文章的一个快照,您可以点击上面的链接看到其他网友对本文的评论。
传送门:46. 全排列。
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ]
回溯算法 + 位掩码(Python 代码、Java 代码)
思路分析:
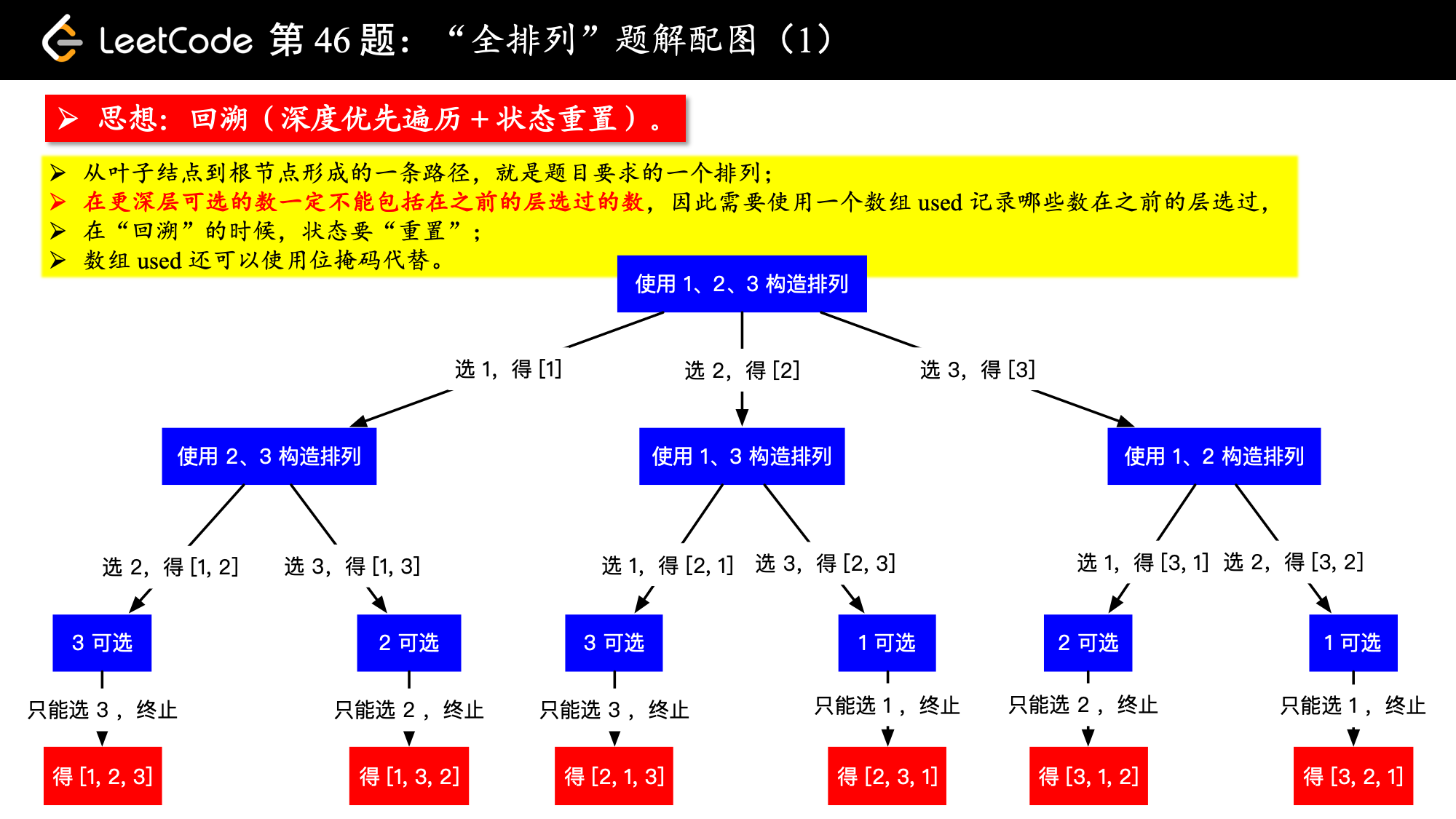
这是一个非常典型的使用 回溯算法 解决的问题。解决回溯问题,我的经验是 一定不要偷懒,拿起纸和笔,画出一个树形结构,思路和代码就会比较清晰了。
方法:回溯算法(深度优先遍历 + 状态重置)
以示例输入: [1, 2, 3] 为例,因为是排列问题,只要我们按照顺序选取数组,保证上一层选过的数字不在下一层出现,就能够得到不重不漏的所有排列,画出树形结构如下图:
 {:width=600}
{:align=center}
{:width=600}
{:align=center}
注意:
1、在每一层,我们都有若干条分支供我们选择。由于是排序问题,之前使用过的数字,在下一层中不能再选取,那么从当前层走到下一层的时候,我们就要问一问自己,哪些数字已经使用过。在编码实现中,可以使用一个布尔型数组 used,用于记录之前(当前路径之前的层)哪些数字使用过。
2、在程序执行到上面这棵树的叶子结点的时候,此时递归到底,方法要返回了,对于这个最后一层选取的数,要做两件事情:(1)释放对它的占用;(2)将它从当前选取放进的排列中弹出。当前,在每一层的方法执行完毕,要返回的时候,都需要这么做。这两点可以简单概括为“状态重置”。
我相信我已经成功地把大家绕晕了,以下是“排列”问题我个人觉得比较好的写法,推荐给大家。
如果序列包含重复数字,这就是 「力扣」第 47 题:全排列 II ,需要做剪枝操作,做法可以参考 回溯 + 剪枝(Python 代码、Java 代码)。
参考代码 1:
Python 代码:
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums):
if len(nums) == 0:
return []
used = [False] * len(nums)
res = []
self.__dfs(nums, 0, [], used, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, nums, index, pre, used, res):
# 先写递归终止条件
if index == len(nums):
res.append(pre.copy())
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if not used[i]:
# 如果没有用过,就用它
used[i] = True
pre.append(nums[i])
# 在 dfs 前后,代码是对称的
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, pre, used, res)
used[i] = False
pre.pop()
Java 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
// curSize 表示当前的路径 path 里面有多少个元素
private void generatePermution(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, int curSize, int len, Stack<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (curSize == len) {
// 此时 path 已经保存了 nums 中的所有数字,已经成为了一个排列
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
path.push(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
generatePermution(nums, visited, curSize + 1, len, path, res);
// 刚开始接触回溯算法的时候常常会忽略状态重置
// 回溯的时候,一定要记得状态重置
path.pop();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[len];
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
generatePermution(nums, used, 0, len, new Stack<>(), res);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4};
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<List<Integer>> permute = solution.permute(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < permute.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(permute.get(i));
}
}
}
技巧:使用位掩码代替 used 数组
参考代码 2:
from typing import List
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
size = len(nums)
if size == 0:
return []
# used = [False] * len(nums)
state = 0
res = []
self.__dfs(nums, 0, size, [], state, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, nums, index, size, pre, state, res):
# 先写递归终止条件
if index == size:
res.append(pre[:])
return
for i in range(size):
if ((state >> i) & 1) == 0:
# 如果没有用过,就用它
state ^= (1 << i)
pre.append(nums[i])
# 在 dfs 前后,代码是对称的
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, size, pre, state, res)
# 状态重置
state ^= (1 << i)
pre.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution()
nums = [1, 2, 3]
result = s.permute(nums)
print(result)
Python 代码:
from typing import List
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
size = len(nums)
if size == 0:
return []
# used = [False] * len(nums)
state = 0
res = []
self.__dfs(nums, 0, size, [], state, res)
return res
def __dfs(self, nums, index, size, pre, state, res):
# 先写递归终止条件
if index == size:
res.append(pre[:])
return
for i in range(size):
if ((state >> i) & 1) == 0:
# 如果没有用过,就用它
pre.append(nums[i])
# 在 dfs 前后,代码是对称的
self.__dfs(nums, index + 1, size, pre, state ^ (1 << i), res)
# 状态重置
pre.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution()
nums = [1, 2, 3]
result = s.permute(nums)
print(result)