LeetCode 第 220 题:“存在重复元素 III”题解
题解地址:滑动窗口 + 二叉搜索树找上下边界(Python 代码、Java 代码)。
说明:文本首发在力扣的题解版块,更新也会在第 1 时间在上面的网站中更新,这篇文章只是上面的文章的一个快照,您可以点击上面的链接看到其他网友对本文的评论。
传送门:220. 存在重复元素 III。
给定一个整数数组,判断数组中是否有两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] 和 nums [j] 的差的绝对值最大为 t,并且 i 和 j 之间的差的绝对值最大为 ķ。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3, t = 0 输出: true 示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1, t = 2 输出: true 示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,5,9,1,5,9], k = 2, t = 3 输出: false
来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate-iii 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
滑动窗口 + 二叉搜索树找上下边界(Python 代码、Java 代码)
思路分析:
1、存在性问题,找到符合题意的数据对即可,所有可能的情况看完以后才返回 false;
2、题目给出了两个限制条件,分别是针对数(nums [i] 和 nums [j] 的差的绝对值最大为 t)和对应的索引(i 和 j 之间的差的绝对值最大为 ķ)的。
由于索引方便定位,因此我们将索引的差值固定,于是问题转化为固定长度(长度为 )的窗口内,是否存在两个值的差距不超过
t,即问题转化为一个“滑动窗口”问题。
由于转化成了“滑动窗口”问题,因此,两个限制条件只剩下一个,即:nums [i] 和 nums [j] 的差的绝对值最大为 t。下面这一点是针对这个限制条件的分析。
3、“数组”和“滑动窗口”问题,我们通常都得遍历,在遍历的过程中,我们试图在“已经出现、但还未滑出滑动窗口”的所有数中查找是否有一个数与当前出现的这个数的差的绝对值最大为 t,这件事情我们换一个说法:
我们在数轴上标出
nums[i]的位置,然后以t为半径画圆,这个圆与nums[i]的左边相交于nums[i] - t,与nums[i]的y右边相交于nums[i] + t,如果我们在遍历中发现,“滑动窗口”内有元素落在[nums[i] - t, nums[i] + t]这个区间内,那么根据第 1 点,直接返回true即可。
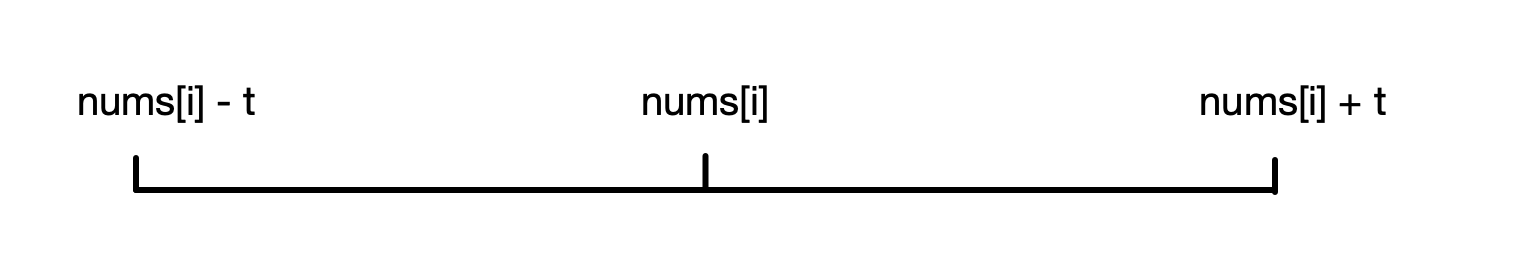
再想想,在“滑动窗口”滑动的过程中,我们需要做什么?
在“滑动窗口”中查找落在
[nums[i] - t, nums[i] + t]这个区间内的元素,存在一个即可。
对于查找问题,我们有什么?顺序查找、二分查找,二叉搜索树,哈希表。
- “顺序查找”可行,“滑动窗口”每滑动一次,就得遍历一遍这个窗口内的元素,效率太低;
- “二分查找”不满足前提条件“数组有序”,故不适用;
- “哈希表”时间复杂度最低,“滑动窗口”每滑动一次,能高效处理添加和删除元素,但我们要找范围,要比较大小,而“哈希表”中的元素丢失了顺序性。
只能下“二叉搜索树”了,看看它能不能胜任:
1、“二叉搜索树”能够“动态地”存储和删除数据,符合“滑动窗口”元素是动态变化,虽然它没有哈希表那么高效;
2、“二叉搜索树”的顺序性就正好符合我们要查找落在 [nums[i] - t, nums[i] + t] 这个区间内的元素这个任务。
这时要用到的两个与我们的任务相关的 API 有:
ceiling(key)函数:返回大于等于key的最小元素,如果不存在,返回空。下面的是这个函数的文档(通过 Intellij IDEA 查看)。
/**
* Returns the least key greater than or equal to the given key,
* or {@code null} if there is no such key.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the least key greater than or equal to {@code key},
* or {@code null} if there is no such key
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map does not permit null keys
*/
K ceilingKey(K key);
floor(key)函数:返回小于等于key的最大元素,如果不存在,返回空。下面的是这个函数的文档(通过 Intellij IDEA 查看)。
/**
* Returns the greatest key less than or equal to the given key,
* or {@code null} if there is no such key.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the greatest key less than or equal to {@code key},
* or {@code null} if there is no such key
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map does not permit null keys
*/
K floorKey(K key);
于是,我们可以
1、在 nums[i] 的左边找一下 ceiling(nums[i] - t),即大于等于 nums[i] - t 的元素是否存在;
2、在 nums[i] 的右边找一下 floor(nums[i] + t),即小于等于 nums[i] + t 的元素是否存在。
参考代码:
说明:
1、在 Java 中,“二叉搜索树”是用红黑树实现的,并且也提供了 ceiling 和 floor 实现,这道题用 Java 语言实现比较方便;
2、由于 Python 中没有“二叉搜索树”实现,以下 Python 示例代码使用了我自己编写的 BST 实现,由于水平有限,没有实现自平衡,故性能较差,供各位参考。
Java 代码:
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Solution {
public boolean containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(int[] nums, int k, int t) {
int len = nums.length;
// 特判
if (len == 0 || k <= 0 || t < 0) {
return false;
}
// 泛型类型为 Long 是提交失败以后看到测试用例以后改的
TreeSet<Long> set = new TreeSet<>();
// 一个一个加进去
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 检测逻辑 1:以当前数为中心,向左边扩展,看看 set 里有没有大于等于 nums[i] - t 的元素
// 大于等于 nums[i] - t ,在这个数上面,故使用天花板函数 ceiling
Long ceiling = set.ceiling((long) nums[i] - t);
// 在 nums[i] 为中心,半径为 t 的左边有元素,因此直接返回 true 即可
if (ceiling != null && ceiling <= nums[i]) {
return true;
}
// 检测逻辑 2:以当前数为中心,向左边扩展,看看 set 里有没有小于等于 nums[i] + t 的元素
// 小于等于 nums[i] + t ,在这个数下面,故使用地板函数 floor
Long floor = set.floor((long) nums[i] + t);
// 在 nums[i] 为中心,半径为 t 的右边有元素,因此直接返回 true 即可
if (floor != null && floor >= nums[i]) {
return true;
}
set.add((long) nums[i]);
// 当 k = 3 时,[0,1,2,3,4],i = 3 的时候就要把 i = 0 删掉了
if (i >= k) {
set.remove((long) nums[i - k]);
}
}
// 遍历以后都找不到符合题意的数据对,就只能返回 False
return false;
}
}
Python 代码:
from typing import List
class Solution:
def containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(self, nums: List[int], k: int, t: int) -> bool:
size = len(nums)
# 特判
if size == 0 or k <= 0 or t < 0:
return False
# 初始化自定义的 bst
bst = Solution.BST()
# 一个一个加进去
for i in range(size):
# 检测逻辑 1:以当前数为中心,向左边扩展,看看 set 里有没有大于等于 nums[i] - t 的元素
# 大于等于 nums[i] - t ,在这个数上面,故使用天花板函数 ceiling
ceiling = bst.ceiling(nums[i] - t)
# 在 nums[i] 为中心,半径为 t 的左边有元素,因此直接返回 true 即可
if ceiling is not None and ceiling <= nums[i]:
return True
# 检测逻辑 2:以当前数为中心,向左边扩展,看看 set 里有没有小于等于 nums[i] + t 的元素
# 小于等于 nums[i] + t ,在这个数下面,故使用地板函数 floor
floor = bst.floor(nums[i] + t)
if floor is not None and nums[i] <= floor:
return True
bst.insert(nums[i])
# 当 k = 3 时,[0,1,2,3,4],i = 3 的时候就要把 i = 0 删掉了
if i >= k:
bst.remove(nums[i - k])
return False
# 以下是自定义的 BST 实现,未实现自平衡,性能较差
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def __str__(self):
# 中序遍历 bst
s = ''
if self.root is None:
return ''
stack = [(1, self.root)]
while stack:
type, node = stack.pop()
if type == 0:
s += str(node.val) + ','
else:
if node.right:
stack.append((1, node.right))
stack.append((0, node))
if node.left:
stack.append((1, node.left))
return s[:-1]
def insert(self, val):
"""
将 val 插入 bst
:param val:
:return:
"""
self.root = self.__insert(self.root, val)
def __insert(self, node, val):
# 在以 node 为根结点的 bst 中,插入 val
if node is None:
return Solution.TreeNode(val)
if val < node.val:
# 注意:不要写成 return self.__insert(node.left, val)
node.left = self.__insert(node.left, val)
return node
elif val > node.val:
# 注意:不要写成 return self.__insert(node.right, val)
node.right = self.__insert(node.right, val)
return node
node.val = val
# 注意:要把 node 返回回去
return node
def remove(self, val):
"""
删除 bst 中等于 val 的结点
:param val:
:return:
"""
if self.root:
self.root = self.__remove(self.root, val)
def __remove(self, node, val):
if node is None:
return None
if val < node.val:
node.left = self.__remove(node.left, val)
return node
if val > node.val:
node.right = self.__remove(node.right, val)
return node
if node.left is None:
new_root = node.right
node.right = None
return new_root
if node.right is None:
new_root = node.left
node.left = None
return new_root
# 用前驱结点 precursor 代替被删除结点
precursor = self.__maximum(node.left)
precursor_copy = Solution.TreeNode(precursor.val)
precursor_copy.left = self.__remove_max(node.left)
precursor_copy.right = node.right
node.left = None
node.right = None
return precursor_copy
def __maximum(self, node):
while node.right:
node = node.right
return node
def __remove_max(self, node):
if node.right is None:
new_root = node.left
node.left = None
return new_root
node.right = self.__remove_max(node.right)
return node
def floor(self, val):
return self.__floor(self.root, val)
def __floor(self, node, val):
if node is None:
return None
if node.val == val:
return node.val
if val < node.val:
return self.__floor(node.left, val)
temp_val = self.__floor(node.right, val)
if temp_val:
return temp_val
return node.val
def ceiling(self, val):
return self.__ceiling(self.root, val)
def __ceiling(self, node, val):
if node is None:
return None
if node.val == val:
return node.val
if val > node.val:
return self.__ceiling(node.right, val)
temp_val = self.__ceiling(node.left, val)
if temp_val:
return temp_val
return node.val