LeetCode 第 211 题:“添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计”题解
题解地址:遇到通配符时递归处理(Python 代码、Java 代码)。
说明:文本首发在力扣的题解版块,更新也会在第 1 时间在上面的网站中更新,这篇文章只是上面的文章的一个快照,您可以点击上面的链接看到其他网友对本文的评论。
遇到通配符时递归处理(Python 代码、Java 代码)
Trie 树又称“前缀树”,它的典型应用对象是字符串,可以用于保存、统计。其特点是:用边表示字符,当走到叶子结点的时候,沿途所经过的边组成了一个字符串。其优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
以下是根据题目示例:"bad"、"dad"、"mad" 组件的 Trie 树,结点值为“1” 表示这是一个单词的结尾。
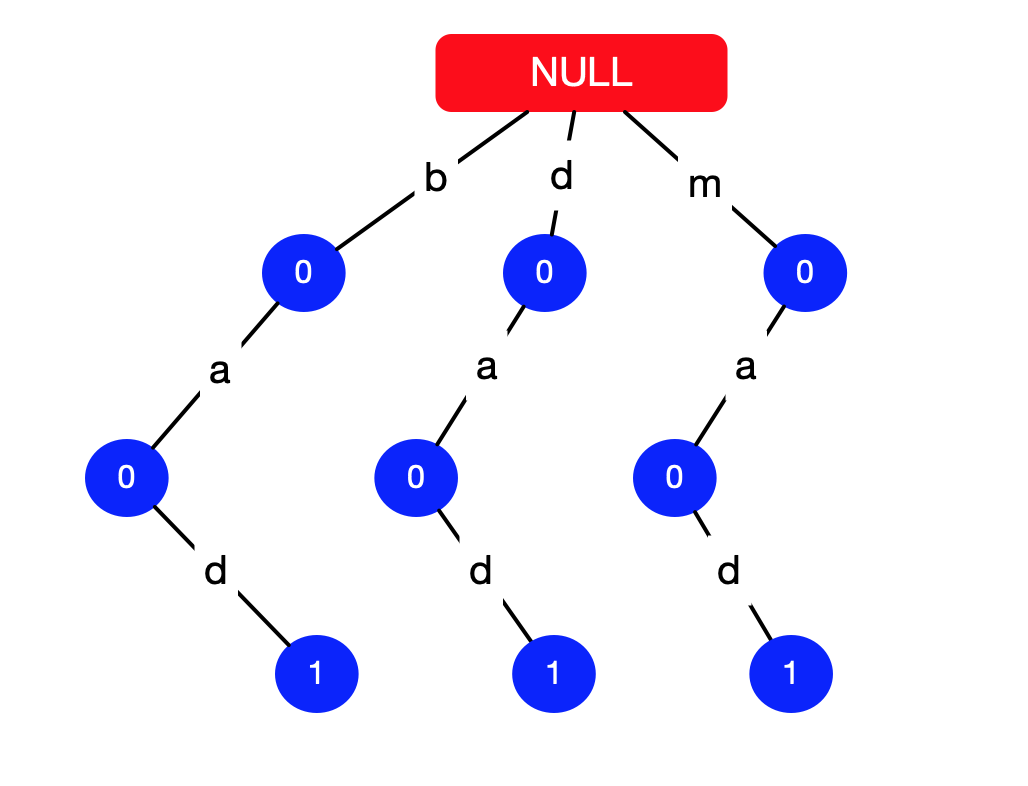 {:width=500}
关于这道问题的难点是通配符
{:width=500}
关于这道问题的难点是通配符 "." 的处理,其实也不难:在遇到 "." 的时候,使用递归方法,将该结点的每一个分支都看过去,只要有一个分支返回 true 就可以了,全部分支都走过去,都没有返回 true 的才返回 false。
对于 Trie 树还不太熟悉的朋友可以先完成 LeetCode 第 208 题:实现 Trie (前缀树),这里要注意的是,一个结点指向孩子结点的“指针”(一般情况下多于 1 个),可以使用数组表示,也可以使用哈希表表示,如果题目中限制了测试用例“所有的输入都是由小写字母 a-z 构成的”,则可以使用数组表示。
1、一个结点指向孩子结点的“指针”们用数组表示;
Python 代码:
class WordDictionary:
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.is_word = False
self.next = [None for _ in range(26)]
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.root = WordDictionary.Node()
def addWord(self, word: str) -> None:
"""
Adds a word into the data structure.
"""
size = len(word)
cur_node = self.root
for i in range(size):
alpha = word[i]
next = cur_node.next[ord(alpha) - ord('a')]
if next is None:
cur_node.next[ord(alpha) - ord('a')] = WordDictionary.Node()
cur_node = cur_node.next[ord(alpha) - ord('a')]
if not cur_node.is_word:
cur_node.is_word = True
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
"""
Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
"""
return self.__match(word, self.root, 0)
def __match(self, word, node, start):
if start == len(word):
return node.is_word
alpha = word[start]
# 关键在这里,如果当前字母是 "." ,每一个分支都要走一遍
if alpha == '.':
# print(node.next)
for i in range(26):
if node.next[i] and self.__match(word, node.next[i], start + 1):
return True
return False
else:
if not node.next[ord(alpha)-ord('a')]:
return False
return self.__match(word, node.next[ord(alpha) - ord('a')], start + 1)
Java 代码:
public class WordDictionary {
class Node {
private Node[] next;
private boolean isWord;
public Node() {
next = new Node[26];
isWord = false;
}
}
private Node root;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public WordDictionary3() {
root = new Node();
}
/**
* Adds a word into the data structure.
*/
public void addWord(String word) {
int len = word.length();
Node curNode = root;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char curChar = word.charAt(i);
Node next = curNode.next[curChar - 'a'];
if (next == null) {
curNode.next[curChar - 'a'] = new Node();
}
curNode = curNode.next[curChar - 'a'];
}
if (!curNode.isWord) {
curNode.isWord = true;
}
}
/**
* Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
return match(word, root, 0);
}
private boolean match(String word, Node node, int start) {
if (start == word.length()) {
return node.isWord;
}
char alpha = word.charAt(start);
if (alpha == '.') {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (node.next[i] != null && match(word, node.next[i], start + 1)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else {
if (node.next[alpha - 'a'] == null) {
return false;
}
return match(word, node.next[alpha - 'a'], start + 1);
}
}
}
2、一个结点指向孩子结点的“指针”们用哈希表表示。
Python 代码:
class WordDictionary(object):
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.is_word = False
self.next = dict()
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.root = WordDictionary.Node()
def addWord(self, word):
"""
Adds a word into the data structure.
:type word: str
:rtype: void
"""
cur_node = self.root
for alpha in word:
if alpha not in cur_node.next:
cur_node.next[alpha] = WordDictionary.Node()
cur_node = cur_node.next[alpha]
if not cur_node.is_word:
cur_node.is_word = True
def search(self, word):
"""
Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
# 注意:这里要设置辅助函数
return self.match(self.root, word, 0)
def match(self, node, word, index):
if index == len(word):
return node.is_word
alpha = word[index]
if alpha == '.':
for next in node.next:
if self.match(node.next[next], word, index + 1):
return True
# 注意:这里要返回
return False
else:
# 注意:这里要使用 else
if alpha not in node.next:
return False
# 注意:这里要使用 return 返回
return self.match(node.next[alpha], word, index + 1)
Java 代码:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
public class WordDictionary {
private Node root;
private class Node {
private boolean isWord;
private HashMap<Character, Node> next;
public Node() {
this.next = new HashMap<>();
}
}
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public WordDictionary() {
root = new Node();
}
/**
* Adds a word into the data structure.
*/
public void addWord(String word) {
Node curNode = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
Character c = word.charAt(i);
if (!curNode.next.containsKey(c)) {
curNode.next.put(c, new Node());
}
curNode = curNode.next.get(c);
}
if (!curNode.isWord) {
curNode.isWord = true;
}
}
/**
* Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
return search(root, word, 0);
}
private boolean search(Node node, String word, int depth) {
if (depth == word.length()) {
// 只要能搜索到最后,就表示文本与模式匹配
// 这一步很容易被忽视
return node.isWord;
}
Character c = word.charAt(depth);
if (c == '.') {
Set<Character> keys = node.next.keySet();
for (Character key : keys) {
Node nextNode = node.next.get(key);
if (search(nextNode, word, depth + 1)) {
return true;
}
}
// 循环都走完都没有找到,那就说明没有
return false;
} else {
if (!node.next.containsKey(c)) {
return false;
}
return search(node.next.get(c), word, depth + 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();
wordDictionary.addWord("bad");
wordDictionary.addWord("dad");
wordDictionary.addWord("mad");
boolean search1 = wordDictionary.search("pad");// -> false
System.out.println(search1);
boolean search2 = wordDictionary.search("bad"); // -> true
System.out.println(search2);
boolean search3 = wordDictionary.search(".ad"); // -> true
System.out.println(search3);
boolean search4 = wordDictionary.search("b.."); //-> true
System.out.println(search4);
}
}